Quick Commerce vs. E-commerce: Which is Right for You?

With the evolution of quick commerce and e-commerce, shopping has become different. Both of these high-tech approaches are revolutionising the shopping process.
E-commerce makes it possible for people from anywhere to shop online. With things delivered within minutes rather than days, quick commerce is furthering this pursuit of convenience.
By 2027, worldwide retail e-commerce sales will hit over $8 trillion. We expect the q-commerce, or fast commerce, market to reach $265.70 billion in 2029. These impressive numbers show the shift in global consumer buying behaviour.
But in the current economy, what really distinguishes q-commerce from e-commerce? Let's look at their qualities, benefits, and how they fulfil contemporary customer demands.
How Quick Commerce Operates and Its Unique Benefits
An emerging trend in e-commerce is quick commerce, or q-commerce. Quick commerce focuses on faster delivery of the product, ideally within minutes or hours. The consumers' growing desire for greater convenience and instant fulfilment is directly addressed by this approach.
The Indian q-commerce market is expected to grow to $9.95 billion by 2029[1]. This growth demonstrates the success and enormous prospects of this method.
Here’s a look at its benefits:
-
Quick Delivery
Speed is the core advantage of quick commerce. This model delivers products within 15-30 minutes, transforming customer expectations and purchasing behaviours. It creates a seamless shopping experience, meeting the demand for instant gratification.
-
Competitive Edge
Quick commerce introduces a unique retail approach that sets businesses apart. By offering swift delivery and diverse products, companies attract convenience-seeking customers. This strategy encourages exploring new brands and product categories.
-
Customer Satisfaction
In a consumer-driven market, meeting expectations is crucial. Quick commerce delivers an experience of simplicity and convenience. It builds customer loyalty by reducing purchasing friction and providing immediate gratification.
-
Increased Profit Margin
Consumer behaviour evolution creates opportunities for adaptable businesses. Quick commerce capitalises on on-demand service needs. It enables companies to charge higher prices for ultra-fast delivery.
-
Lower Logistics Cost
Quick commerce optimises local delivery through compact warehouses and vendor partnerships. This approach reduces shipping costs, accelerates delivery times, and creates a responsive distribution system.
Benefits of E-commerce and How it Works
Buying and selling goods and services, mostly online, is known as traditional e-commerce. It is essentially online purchasing. Amazon, Flipkart, and Ajio are some of India's top e-commerce platforms.
The following are the main features of e-commerce:
-
Lower Overhead Costs
Compared to running a physical store, operating an online store is less expensive. E-commerce does not require traditional retail costs like space and manpower. Your main expenses are promotion and web hosting.
-
No Need for Physical Stores
E-commerce removes the financial strain of physical stores. No more spending money on electricity, security, or city retail locations. You can run an online store from anywhere.
-
Massive Audience Reach
Internet businesses are not restricted by traditional retail's regional boundaries. Potential customers from other areas can view your products.
-
Increased Scalability
Physical area restrictions on business expansion are eliminated by e-commerce. Increase your product and inventory selection without having to worry about moving or modernising your premises. Scaling is relatively simple with digital platforms.
-
Easier Logistics Tracking
Order, shipment, and return tracking are made considerably simpler with electronic records. You can effectively analyse sales trends and outsource fulfilment procedures. Everything becomes easier to understand and control.
Quick Commerce vs. E-commerce: What Are the Key Differences?
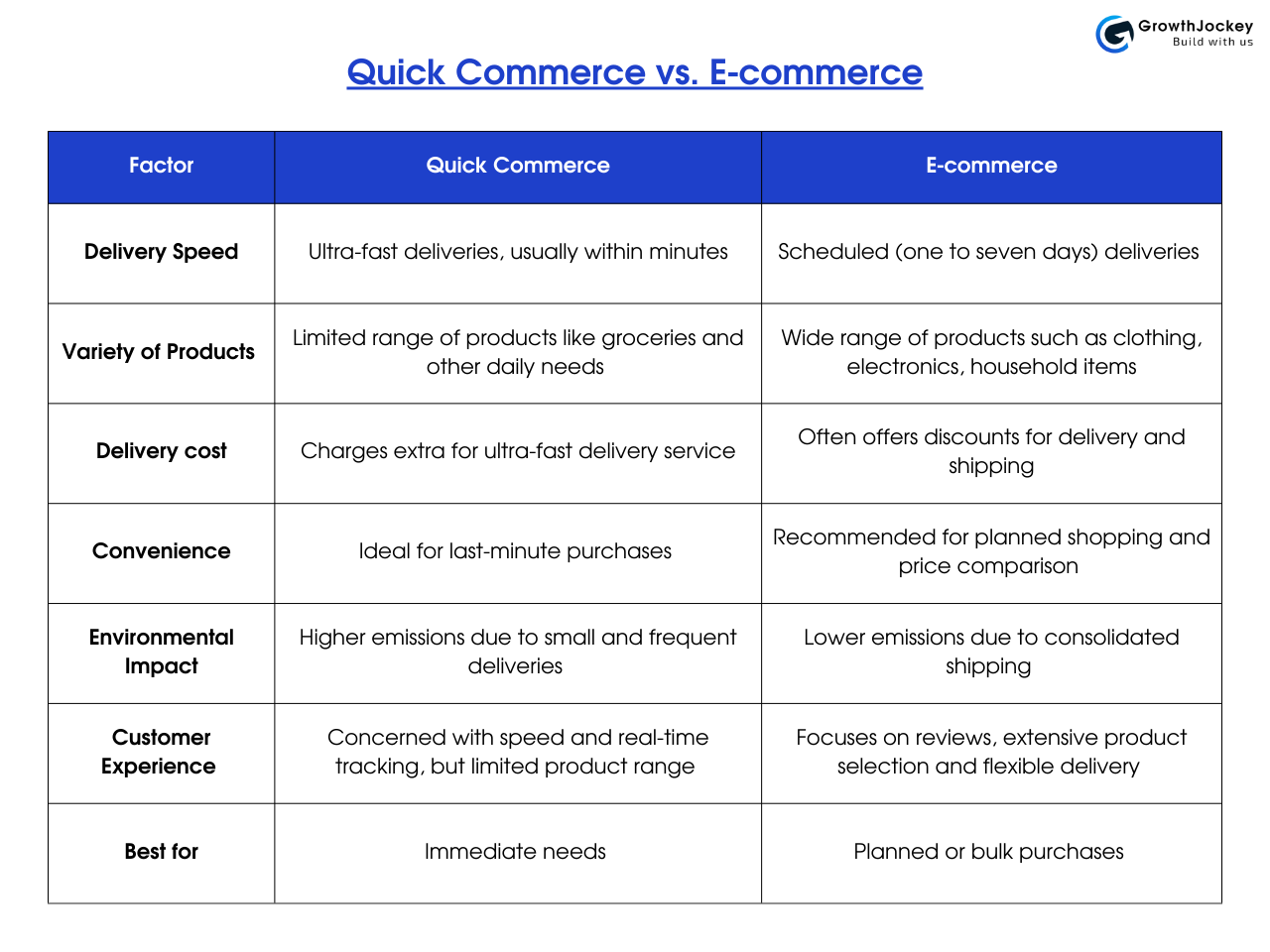
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Quick Commerce vs. E-commerce
Choosing between quick commerce and e-commerce isn’t about right or wrong—it’s about what aligns with your goals. Each model has its strengths, and understanding the key factors can help you decide which one is the better fit for your business.
Let’s break it down:
-
Product Range
Your business offering dictates your platform choice. Quick commerce works best for limited, time-sensitive products like groceries and medicines. E-commerce suits diverse products such as electronics and fashion that don't require immediate delivery.
-
Customer Expectation
Understanding your buyer persona is key to selecting the right platform. If your customers demand perishable items, you need quick commerce. Durable goods fit traditional e-commerce models.
-
Logistics and Infrastructure
Your existing logistics network determines your platform viability. Quick commerce requires robust local warehouse partnerships and efficient delivery systems. Ensure you have the necessary infrastructure before committing.
-
Operating Cost
Both platforms are more cost-effective than physical stores. However, each has unique expense structures. Analyse your specific operational costs to make an informed decision.
-
Profit Margin
Consider the profitability of each model. Do you know why? Quick commerce can move small items quickly, potentially generating faster turnover. E-commerce might offer higher-value transactions with lower operational complexity.
-
Technological Integration
Your online store needs proper technology integration. Think about payment systems, checkout processes, and digital infrastructure. Choose a platform that matches your technological capabilities.
Examples of Leading E-commerce and Quick Commerce Companies in India
-
Q-commerce
1. Blinkit
Blinkit, an Indian q-commerce platform, delivers groceries in minutes. It uses small warehouses to ensure fast and efficient service. Blinkit’s quick delivery model meets customer demands for instant gratification.
2. Zepto
Zepto is known for 10-minute deliveries across Indian cities. It focuses on small, high-demand products like groceries and snacks. Zepto’s efficiency has set new benchmarks for speed in retail.
-
E-commerce
1. Amazon
Amazon offers a vast product range and flexible delivery options. It uses advanced logistics for fast, reliable shipping across regions. Amazon’s focus on variety makes it a global e-commerce leader.
2. Flipkart
Flipkart is a top Indian e-commerce brand with diverse offerings. Its user-friendly app makes shopping accessible to millions of consumers. Flipkart’s wide product range attracts customers across all demographics.
How GrowthJockey Can Help You Choose and Implement the Best Model
GrowthJockey helps businesses choose between quick commerce vs. e-commerce. We analyse your goals and market needs thoroughly.
Our team ensures quick implementation of the chosen model. Whether you prioritise speed or variety, we provide tailored solutions.
As your business evolves, choosing the right commerce model becomes crucial. Our consultants are ready to walk you through the decision-making process, offering data-driven insights and industry expertise to help you make an informed choice.
Get started with expert guidance from GrowthJockey today!
FAQs
1. What is the difference between q-commerce and e-commerce?
Quick commerce delivers instantly and suits urgent customer needs. E-commerce provides more products and flexible delivery options. Decide based on your requirements.
2. Which has better payment options, e-commerce or m-commerce?
E-commerce requires a computer and uses traditional payment methods. Credit cards and other conventional payment methods are usually used in e-commerce purchases.
M-commerce supports mobile wallets and contactless payments for convenience.
3. How is social commerce different from e-commerce?
Social commerce uses engaging and user-generated content (UGC). E-commerce does not focus on interactions as much. It relies on branded content.








